Electric Vehicle Charging Station Power Supply Optimization with V2X Capabilities Based on Mixed-Integer Linear Programming
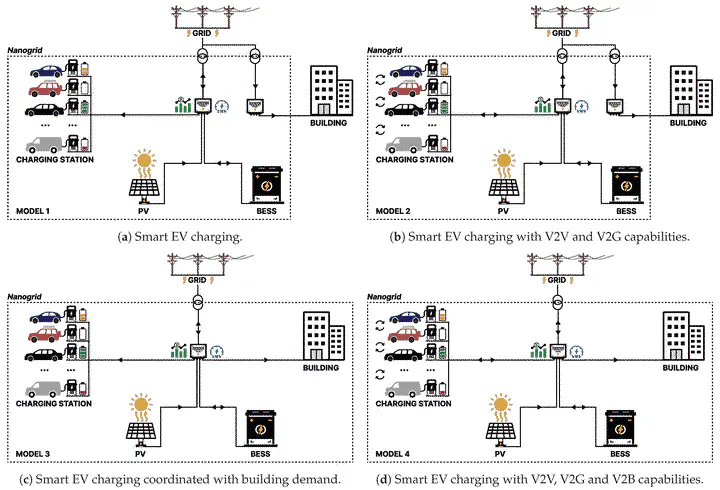
Abstract
The European Union is committed to both lowering greenhouse gas emissions and promoting the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) on its roads. To achieve these goals, it is imperative to speed up the development of the charging infrastructure as well as to ensure the effective integration of the charging infrastructure into distribution networks. Given that EV charging costs significantly contribute to the total cost of owning an EV, it is important to hedge against rising electricity prices and ensure affordable charging for the end users. Connecting solar power plants and battery storage to the electric vehicle charging stations (EVCSs) serves as a measure of hedging against potential future electricity price increases but also as an option that can contribute to reducing impact on the distribution network loading. In addition to this, connecting EVCS through grid connections of existing consumers (office/residential buildings, shopping malls, etc.) can reduce grid connection costs for EVCS but also contribute to electricity cost reduction for both EVCS and existing end consumers. Additionally, by integrating advanced charging strategies like the vehicle-to-everything (V2X) approach, the overall charging costs can be reduced even further. This paper focuses on optimizing the power supply and operation of EVCS by considering strategic investments in grid connection, photovoltaic plants, and battery energy storage. The research explores the potential savings derived from reduced energy/charging costs, along with the reduction in peak power expenses for different power supply options. In addition to this, the research explores the effect of different EV charging strategies as well as EVCS grid connection on optimal investments and total system costs. The combined investment and energy management problem is focused on determining the optimal EVCS power supply and operation while minimizing total investment and operation expenditures over the project lifetime. The underlying optimization problems for different supply scenarios are cast as mixed-integer linear programming problems that can be solved efficiently. The results show the influence of different grid connection options and EV charging strategies on the joint operation and costs of EVCS and existing buildings.